Butterfly Valves
A butterfly valve is a rotary motion valve. The main purpose of butterfly valve is used to stop, regulate, and start fluid flow. This type of valve is easily and quickly operated because there is a 90 degree rotation of the handle which moves the disk from a fully closed to fully opened position.
Butterfly valves are available in various sizes and materials. Infact, the larger sized butterfly valves are actuated by hand wheels which are connected to the stem through gears and they provide mechanical advantage at the expense of speed.
 Materials
used:
Materials
used:
- Mild Steel
- Stainless Steel
- Bronze
- Gun Metal
- Cast Iron
- Forged Steel
- Carbon Steel
- Plastic
- Polypropylene
- Aluminum etc.
Characteristics of butterfly valves:
The following are characteristics for butterfly valves when used for
modulating service and can also be considered as general control valve
terms:
- Linear: The flow rate is proportional to the amount of
disk travel.
- Equal percentage: This characteristic means that equal
increments of valve flow produce equal percentage changes in
flowrate. This is done on the basis of relation to the flowrate that
existed at the previous travel position.
- Quick opening: Flowrate through the butterfly valve
increases very rapidly for incremental changes in valve flow when
valve position is almost closed.
Buying Tips
The selection of the appropriate butterfly valve depends on the characteristics which in turn are dependent on the needs of the system. There are several factors to be considered for an effective flow rate and hence a complete system analysis is required to determine which is the optimum characteristic. Certain
rules of thumb are:
- Choose equal percentage, if in doubt about the preferred characteristic. Such a choice results in a perfect match.
- The quick-opening characteristic is hardly employed for control applications, except for pressure-relief applications.
- For liquid applications, the use of the linear characteristic provides the best results if greater than 25% of system pressure drop is available to the valve at maximum flow conditions.
- If the butterfly valve is used for control of pressure, the use of equal percentage characteristic is preferred.
- For gas applications also, the use of the equal percentage characteristic is preferred.
- For large-volume systems, the use of the linear characteristic is preferred.
- Other features to consider are as follows:
- Materials
- Standard
- Design
- Durability
- Media
- Pressure rated
- Operation: Hand lever, Gearbox, Actuator
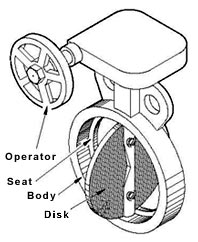 Parts
of a butterfly valve:
Parts
of a butterfly valve:
The butterfly valve consists of only five main components. They are as
follows:
- Body: These valves have bodies that fit between two pipe
flanges.
- Disc: The disk is the flow closure member of a butterfly
valve.
- Stem: The stem of the butterfly valve is either a
one-piece shaft or a two-piece, also known as split-stem design.
- Seat: The seat of a butterfly valve utilizes an
interference fit between the disk edge and the seat to close or to
shutoff.
- Operator
Types of butterfly valves:
There are three types of butterfly valves:
- Resilient butterfly valve: This has a flexible rubber
seat.
- High performance butterfly valve: This double eccentric
in design.
- Tricentric butterfly valve: This is with a metal seated
design.
Uses of Butterfly valves:
Butterfly valves are considered to be the most economical and reliable
type of pipe valves. Technological innovations combined with the simple
design of the butterfly valve has made it a dependable, economical and
flexible solution to a variety of industrial flow control needs. These
valves have many advantages over other valves like gate, globe, plug,
and ball valves, especially in large valve applications. The most
obvious advantages are savings in weight, space, and cost. The
maintenance cost is low because there are a less number of moving parts
and there are no pockets to trap fluids. They are widely used in water
distribution and waste water processing.
The points mentioned below will be a guide for the buyers:
 Materials
used:
Materials
used:
 Parts
of a butterfly valve:
Parts
of a butterfly valve: